The Flexible Trading Tool
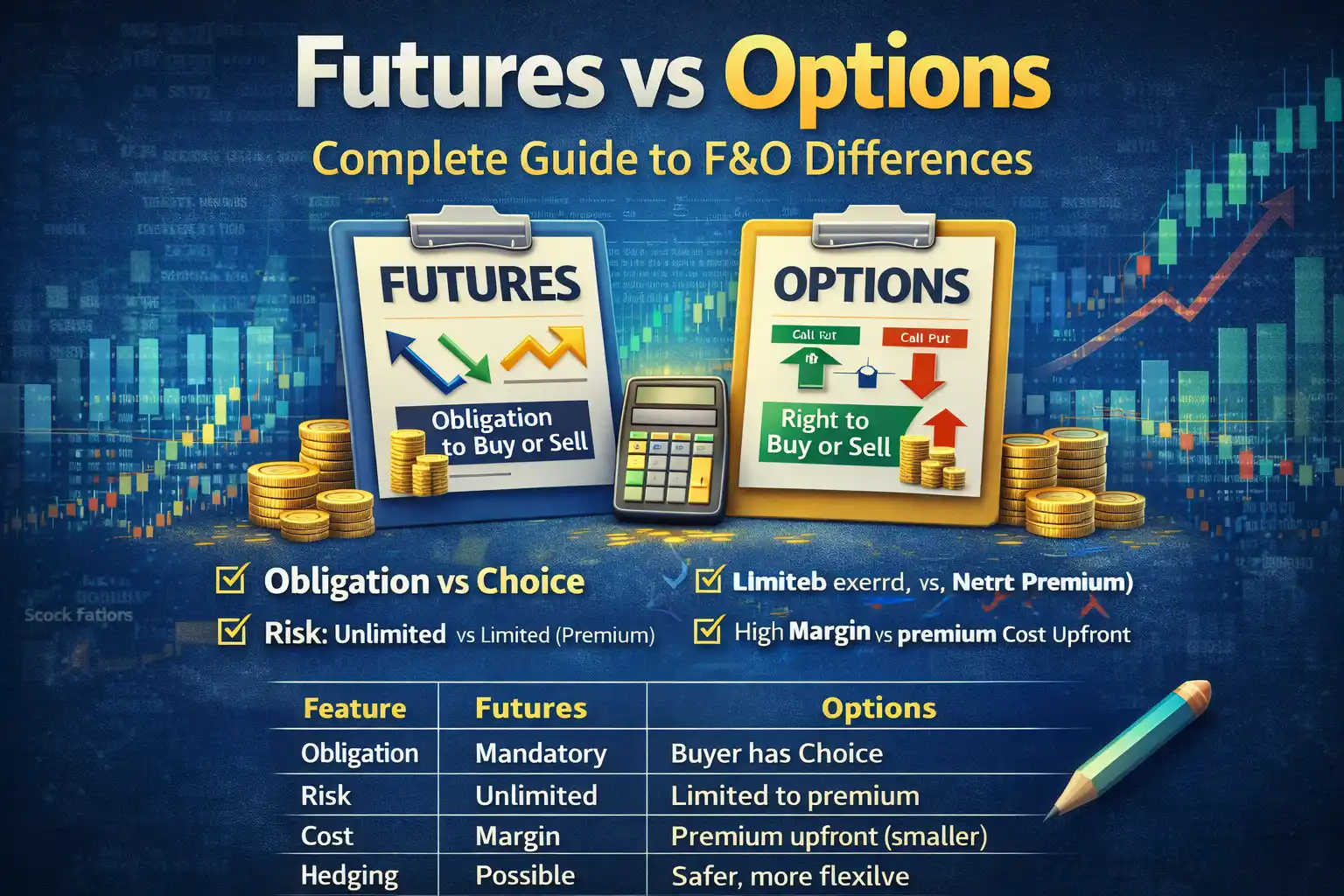
If you have learned about Futures, you know that Futures involve an obligation. That means you must buy or sell the asset when the contract expires.
Options are different. With options, you get the right, but not the obligation, to buy or sell an asset at a predetermined price. This flexibility makes options a powerful and strategic tool for traders and investors.
With options, you can:
- Profit whether the market goes up or down
- Limit your losses
- Hedge existing positions in your portfolio
Options – Definition
An Option is a financial contract that gives the buyer the right, but not the obligation, to buy or sell an underlying asset.
Simple Explanation:
The buyer has a choice; the seller has an obligation if the buyer decides to exercise the option.
Example:
Reliance shares are currently trading at ₹2,500.
- Call Option: Right to buy at ₹2,500 within 1 month
- Put Option: Right to sell at ₹2,500 within 1 month
If the market moves in your favor → profit
If the market moves against you → loss is limited to the premium paid
Key Point: Options limit risk for buyers while providing significant profit potential.
Call Option – Right to Buy
A Call Option gives the buyer the right to buy an asset at a strike price on or before the expiry date.
Example:
- Strike Price: ₹2,500
- Premium: ₹50
- Lot Size: 100 shares
Scenario 1 – Profit:
Market price at expiry = ₹2,600
- Profit = (2,600 – 2,500 – 50) × 100 = ₹5,000
Scenario 2 – Loss:
Market price at expiry = ₹2,450
- Loss = Premium × Lot size = 50 × 100 = ₹5,000
Key Point:
- Maximum loss = Premium
- Maximum profit = theoretically unlimited
Explanation:
Call options allow buyers to benefit from rising markets, while limiting potential losses to the premium paid.
Put Option – Right to Sell
A Put Option gives the buyer the right to sell an asset at a strike price on or before the expiry date.
Example:
- Strike Price: ₹2,500
- Premium: ₹50
- Lot Size: 100 shares
Scenario 1 – Profit:
Market price at expiry = ₹2,400
- Profit = (2,500 – 2,400 – 50) × 100 = ₹5,000
Scenario 2 – Loss:
Market price at expiry = ₹2,550
- Loss = Premium × Lot size = 50 × 100 = ₹5,000
Key Point:
- Maximum loss = Premium
- Profit is limited to the difference between strike price and market price minus premium
Explanation:
Put options allow buyers to profit from falling markets while limiting potential losses to the premium paid.
Key Features of Options
- Right but Not Obligation:
Buyers have the choice to exercise the option; sellers have the obligation if the buyer exercises. - Premium:
Paid upfront by the buyer, representing maximum risk; received by the seller as profit. - Call & Put:
- Call = Right to Buy → Profitable if market rises
- Put = Right to Sell → Profitable if market falls
- Strike Price & Expiry Date:
- Strike price = price at which the option can be exercised
- Expiry date = last day the option can be exercised
- Leverage:
Small premium payment provides large market exposure, similar to Futures, but risk is limited. - Risk Control:
Maximum loss for the buyer is limited to the premium paid, regardless of market movement.
Importance of Options
- Profit in Any Market Direction: Call options for up markets, Put options for down markets
- Risk Control: Buyers’ losses limited to premium
- Flexibility & Strategies: Combine multiple options (spreads, straddles) for advanced trading
- Hedging: Protect existing portfolio from market falls
Example:
You own 100 Reliance shares → Market falls → Buy Put options to reduce losses
Simple Call & Put Example – Step by Step
Scenario: Reliance shares = ₹2,500, Lot size = 100, Premium = ₹50
| Option Type | Strike Price | Market Price at Expiry | Profit / Loss |
| Call | 2,500 | 2,600 | ₹5,000 |
| Call | 2,500 | 2,450 | –₹5,000 |
| Put | 2,500 | 2,400 | ₹5,000 |
| Put | 2,500 | 2,550 | –₹5,000 |
Observation:
- Buyer’s maximum loss = Premium
- Profit depends on market movement
Outcome
Options trading is a flexible and strategic financial tool providing profit opportunities and risk management.
Summary:
- Call Option: Right to buy; profitable when the market rises
- Put Option: Right to sell; profitable when the market falls
- Risk: Maximum loss for buyers = Premium
- Use: Hedging, speculation, and advanced strategies
After understanding Options, you are ready for combined Futures & Options strategies and advanced F&O trading.