हिंदी में पढ़ने के लिए मेनू बार से हिंदी भाषा चयन करें।
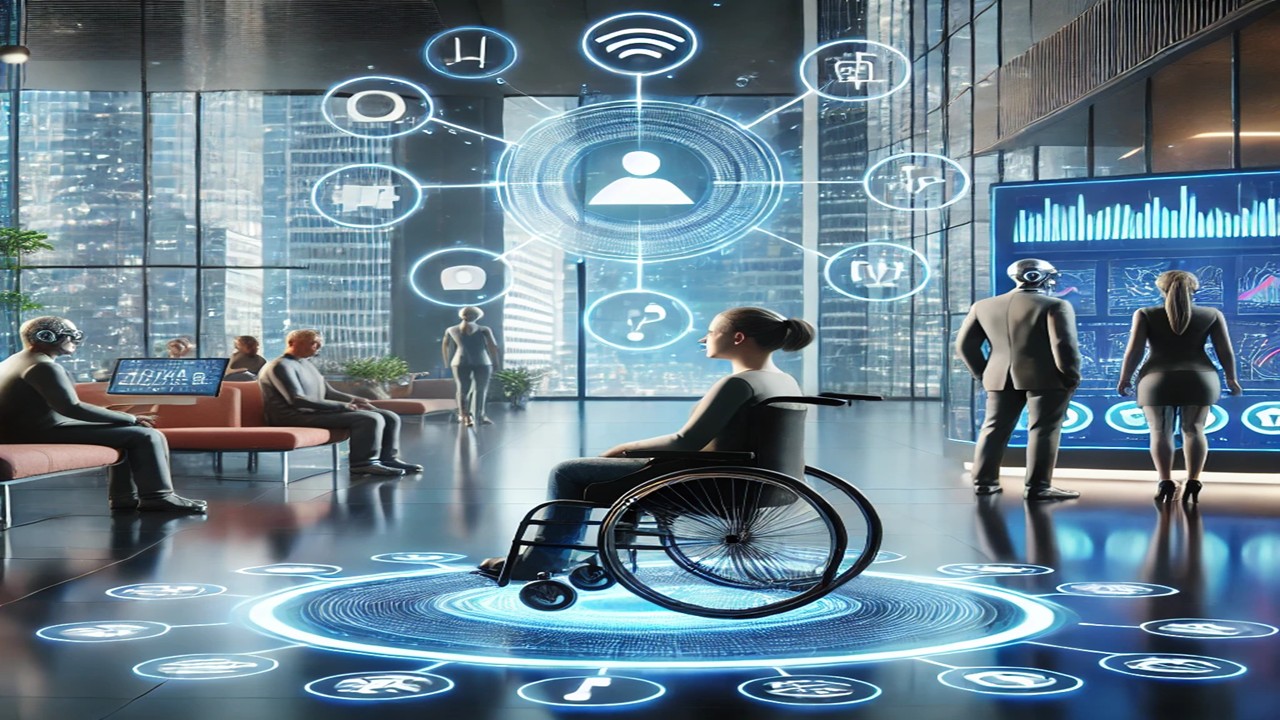
Imagine a world where barriers cease to exist—a world where individuals with disabilities are empowered to live, work, and dream without limitations. For years, this seemed like a distant vision, but today, technology is transforming that dream into reality. A silent yet powerful revolution is unfolding in the realm of Assistive Technologies (AT), reshaping lives and bridging gaps.
As we delve into this fascinating topic, let’s explore how these innovations are creating a more inclusive world, their growing demand, the role of key players in this space, and the future possibilities that could redefine accessibility.
What Are Assistive Technologies?
Assistive Technologies refer to tools, devices, and software designed to help individuals with disabilities perform tasks that may otherwise be challenging or impossible. These technologies empower users to overcome physical, sensory, or cognitive limitations. From prosthetics and wheelchairs to screen readers and advanced AI tools, AT is a broad category that caters to diverse needs.
Key Categories of Assistive Technologies
- Mobility Devices:
These include powered wheelchairs, exoskeletons, and mobility scooters that help individuals with movement challenges regain their independence. Advanced prosthetic limbs, controlled by neural signals, have also revolutionized mobility. - Visual and Hearing Aids:
- For the Visually Impaired: Devices like screen readers, Braille displays, and smart glasses enable visually impaired individuals to interact with their environment and access information.
- For the Hearing Impaired: Hearing aids, cochlear implants, and live transcription apps like Ava provide seamless communication experiences.
- Communication Aids:
Augmentative and Alternative Communication (AAC) devices, such as speech-generating tools, allow individuals with speech impairments to express themselves effectively. - Cognitive Assistance:
Tools like memory aids and task management apps assist people with cognitive impairments or neurological disorders in managing daily activities. - Home Automation for Accessibility:
Smart home systems, voice-controlled devices, and automated lighting or door systems ensure that homes are more accessible for individuals with physical disabilities. - Education-Focused Tools:
Tools like text-to-speech software, voice recognition, and digital learning platforms make education inclusive for students with disabilities.
Rising Demand and Future Demand for Assistive Technologies
Current Demand:
The demand for assistive technologies is growing exponentially due to:
- Increased awareness about disability rights.
- Aging populations worldwide, particularly in developed nations.
- Advancements in technology making these devices more affordable and accessible.
Future Demand:
By 2030, the demand for assistive technologies is expected to skyrocket, driven by:
- Increased focus on workplace inclusivity.
- The rise in chronic health conditions and disabilities due to lifestyle and aging.
- Evolving regulations mandating accessibility in public spaces and digital platforms.
For example, AI-powered assistive tools such as wearable devices that translate sign language into speech or devices that convert thoughts into commands for prosthetics are poised to become mainstream.
Benefits of Assistive Technologies
- Empowerment:
Individuals gain independence and control over their lives. - Inclusivity:
It ensures that people with disabilities can participate fully in education, employment, and social activities. - Improved Quality of Life:
These technologies enhance daily living by providing solutions tailored to unique needs. - Economic Impact:
Assistive technologies reduce dependency, enabling individuals to contribute to the economy and save healthcare costs. - Enhanced Productivity:
In workplaces, assistive tools improve efficiency and unlock the potential of employees with disabilities.
Companies Leading the Way in Assistive Technologies
Several companies are making significant strides in the assistive technology landscape:
- Microsoft:
Known for its inclusive initiatives, Microsoft’s Seeing AI app helps visually impaired individuals identify objects, read text, and navigate their surroundings. - Google:
Google’s Live Transcribe app converts speech into text in real-time, while its accessibility features in Android empower users with various disabilities. - Apple:
Apple offers a range of assistive features, such as VoiceOver for the visually impaired and Switch Control for individuals with physical disabilities. - Boston Dynamics:
Known for robotics, they’re working on mobility solutions like advanced exoskeletons. - ReWalk Robotics:
A pioneer in wearable robotic exoskeletons, enabling individuals with spinal cord injuries to walk again. - Oticon:
Innovating in hearing aids with AI-powered devices that adapt to different sound environments. - Tobii Dynavox:
A leader in AAC devices, providing tools for individuals with speech impairments.
Future Possibilities in Assistive Technologies
The future of assistive technologies is incredibly promising, with innovations in the pipeline that could redefine accessibility:
- AI and Machine Learning:
Advanced AI algorithms will enable real-time language translation for sign language or Braille-to-text conversion. - Brain-Computer Interfaces (BCI):
Devices that interpret neural signals to control prosthetics or communicate thoughts directly into text. - Wearable Devices:
Smart glasses and haptic wearables will allow sensory feedback and environment interaction like never before. - Personalized 3D Printing:
Custom prosthetics and mobility aids created through 3D printing will make these devices affordable and highly tailored to individual needs. - Self-Navigating Mobility Devices:
Wheelchairs equipped with sensors and AI for autonomous navigation in crowded spaces. - Digital Avatars and Virtual Assistants:
Avatars that help individuals with cognitive challenges manage schedules, communicate, or even assist in social situations.
Challenges to Address
Despite advancements, some barriers need to be overcome:
- Cost: High prices of assistive devices make them inaccessible to many.
- Awareness: A lack of awareness among users and policymakers limits adoption.
- Customization: Devices need to be adaptable to diverse user needs and environments.
Conclusion
Assistive technologies are more than just tools—they are lifelines that empower individuals, enhance lives, and promote equality. As innovations continue to bridge the gap between ability and disability, the future holds unparalleled possibilities.
With major tech companies, startups, and researchers investing heavily in this space, we are moving closer to a world where everyone, regardless of their abilities, has equal opportunities to thrive. The silent revolution of assistive technologies is not just about technology; it’s about humanity’s commitment to creating an inclusive and equitable society.