हिंदी में पढ़ने के लिए मेनू बार से हिंदी भाषा चयन करें।
When the Ocean Becomes a Power Plant
In today’s world, we face two major problems:
- The rising demand for clean energy
- The urgent need to reduce carbon emissions
Among various renewable energy options, there is one powerful yet less-known solution—Ocean Thermal Energy Conversion (OTEC).
This technology uses the temperature difference between the warm upper layers and cold deep layers of the ocean to produce electricity.
Unlike solar or wind energy, OTEC can work 24 hours a day, 365 days a year, because the ocean’s temperature layers are always present—day or night, sunny or cloudy.
🌟 Benefits of OTEC
1. Continuous Power Supply
OTEC plants can produce electricity non-stop since ocean water temperatures remain fairly constant.
2. Zero Carbon Emissions
OTEC uses ocean water, not fossil fuels. So it’s completely clean and environmentally friendly.
3. Fresh Drinking Water (Desalination)
Some OTEC systems can turn salty seawater into freshwater, which is helpful in coastal and island regions.
4. Aquaculture and Cooling
Cold deep-sea water can be used in fish farming and to cool buildings or data centers
❓ What is OTEC?
Ocean Thermal Energy Conversion (OTEC) is a process that generates power using the difference in temperature between warm surface seawater (around 25°C) and cold deep seawater (around 5°C).
This 20°C temperature difference creates a cycle where energy is extracted to run turbines and produce electricity.
This technology works best in tropical ocean regions, where the surface is warm and the deep sea remains cold year-round.
⚙️ How Does OTEC Work?
There are three main types of OTEC systems:
🟠 1. Closed Cycle OTEC
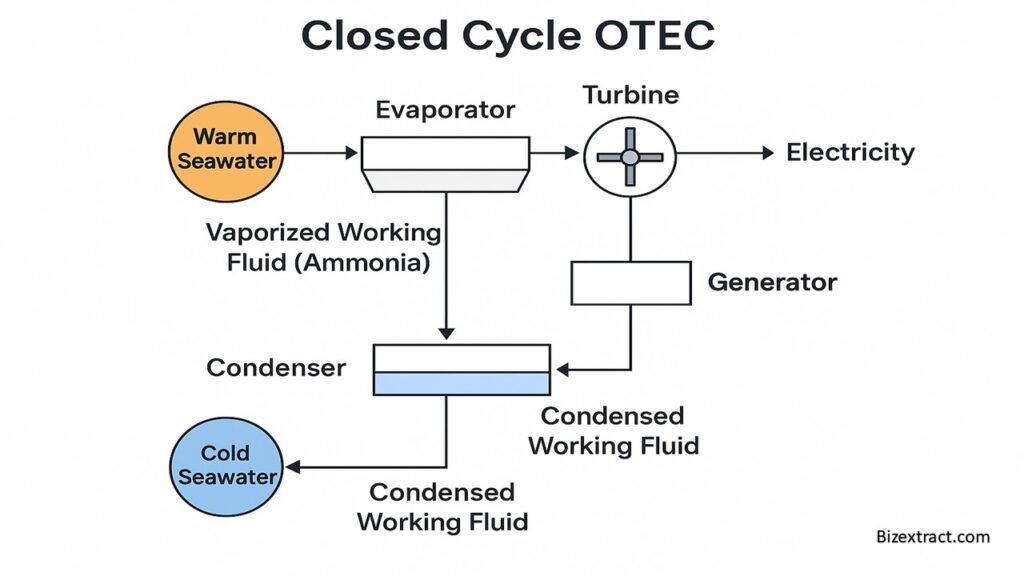
Process:
- A special fluid like ammonia (which boils at low temperatures) is used.
- Warm surface water heats the ammonia, turning it into gas.
- The gas spins a turbine → electricity is generated.
- Cold deep-sea water cools the gas back into liquid.
🔁 This cycle repeats constantly.
➡️ Called “closed” because the fluid stays inside a sealed system.
🔵 2. Open Cycle OTEC
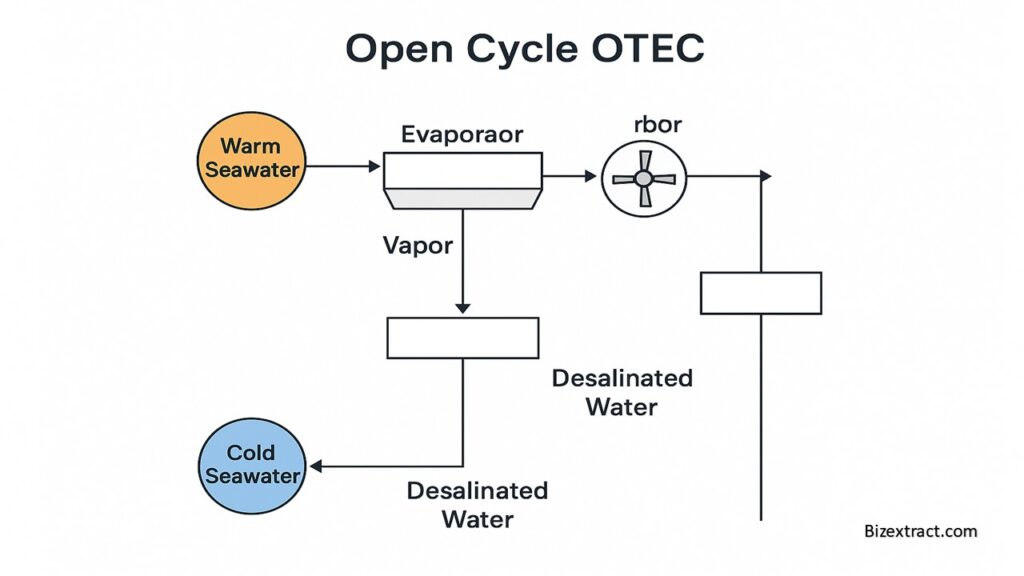
Process:
- Warm seawater is placed in a low-pressure chamber.
- It boils naturally (without heat) into steam.
- The steam spins a turbine → electricity is generated.
- Cold water then turns the steam into freshwater.
💧 Bonus: This method also provides drinking water.
➡️ Useful in places facing water shortages.
🟢 3. Hybrid Cycle OTEC
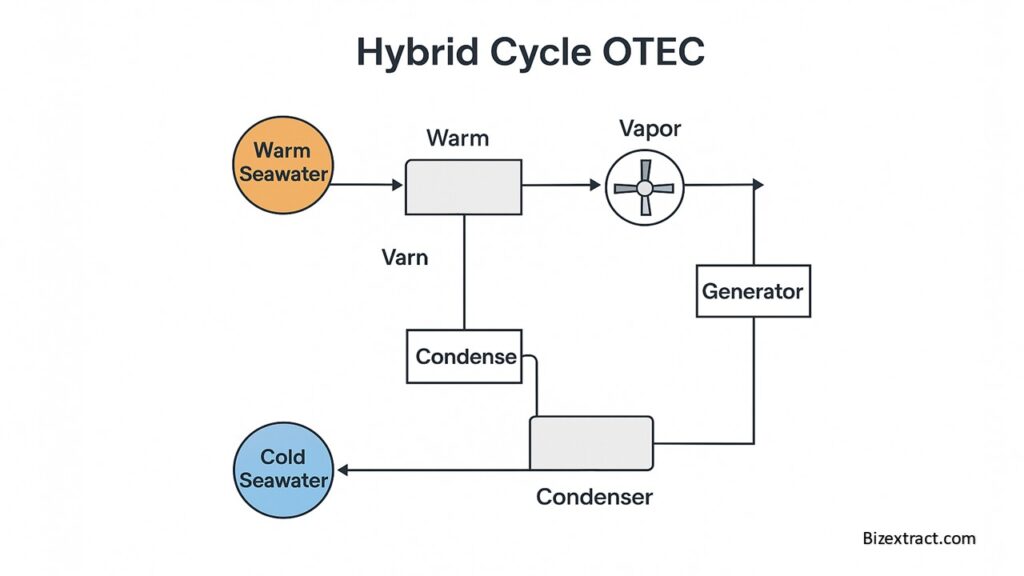
This method combines the closed and open cycles:
- One system produces electricity (closed),
- The other creates freshwater (open).
It provides both power and clean water together.
🌍 Which Countries and Companies Are Working on OTEC?
🇺🇸 USA (Hawaii)
- Hawaii developed the world’s first commercial OTEC plant.
- Companies like Makai Ocean Engineering and Ocean Era are active.
- Hawaii’s ocean is ideal for OTEC.
🇯🇵 Japan
- Japan has led OTEC research for decades.
- Saga University and IHI Corporation are key players.
- Japan’s many islands make it perfect for ocean energy.
🇮🇳 India
- NIOT (National Institute of Ocean Technology) is planning a floating OTEC plant in Lakshadweep.
- It could be Asia’s first floating OTEC system.
- India’s long coastline offers huge potential.
🇫🇷 France (La Réunion)
- In La Réunion Island, Akuo Energy and DCNS Group planned a 10 MW OTEC plant.
- France is exploring tropical ocean zones for clean energy.
Challenges of OTEC
| 🚧 Challenge | 🧾 Explanation |
| High Cost | Setting up pipes and plants in the ocean is expensive. |
| Engineering Complexity | Deep-sea pressure, corrosion, and weather make it technically difficult. |
| Low Efficiency | The temperature difference is small, so energy output is limited. |
| Location-Specific | OTEC works only in regions near the equator with stable warm-cold water layers. |
Additional Uses of OTEC
💧 1. Drinking Water
The open-cycle system produces desalinated water—very useful for island and coastal communities.
🐟 2. Aquaculture
The cold water brought up from deep sea supports fish farming, increasing productivity.
❄️ 3. Cooling Buildings
Deep seawater can be circulated through buildings for natural air conditioning.
⚡ 4. Hydrogen Production
OTEC plants can help in producing green hydrogen, a clean fuel for the future.
OTEC – Clean Power from the Depths of the Sea
OTEC is a revolutionary clean energy technology that turns the ocean’s temperature difference into reliable electricity.
Unlike solar or wind power, which depend on weather, OTEC works round the clock—making it perfect for island nations and tropical regions.
While challenges like high costs and technical complexity remain, global interest and research are growing fast. If governments and companies continue to invest, OTEC could become a vital part of our future energy mix.