हिंदी में पढ़ने के लिए मेनू बार से हिंदी भाषा चयन करें।
🌱 A New Era of Healing: Can the Body Regrow Its Own Organs?
Imagine a future where lost limbs regrow naturally… where a burned patch of skin rebuilds itself… where people waiting for organ transplants are treated using their own cells. This is not science fiction anymore. Thanks to a groundbreaking field known as regenerative medicine, the body may soon be able to heal itself — not just cuts and wounds — but entire organs.
The concept of the body rebuilding itself, once a far-fetched dream, is now turning into reality through a combination of biology, biotechnology, and advanced engineering. This technology is opening doors to a new kind of healthcare, where healing comes from within.
🔬 What is Regenerative Medicine?
Regenerative medicine is a branch of biomedical science focused on regrowing, repairing, or replacing damaged tissues and organs using the body’s natural healing capabilities. It often involves the use of stem cells, tissue scaffolding, and 3D bioprinting technologies to stimulate the body to regrow parts that are otherwise permanently damaged.
It has the potential to:
- Replace damaged organs
- Repair injured tissues
- Heal wounds faster
- Reverse degenerative diseases
🧪 How Did This Technology Begin?
The foundation of regenerative medicine lies in stem cell research, which began gaining serious attention in the late 1990s. In 1998, human embryonic stem cells were first successfully grown in the lab. In 2006, Shinya Yamanaka, a Japanese scientist, discovered how to create induced pluripotent stem cells (iPS cells) from adult cells — earning him the Nobel Prize. This discovery changed everything. Scientists realized that if human cells could be reprogrammed to become any type of cell — including heart, skin, liver, or nerve — then perhaps entire organs could be regrown using a patient’s own cells
🌍 Which Countries Are Leading the Research?
Many countries are investing heavily in regenerative medicine:
- United States: Institutions like Harvard, Stanford, and the Wake Forest Institute for Regenerative Medicine are leading global innovation.
- Japan: A pioneer in iPS cell research, with Kyoto University taking the lead.
- Germany: Known for advancements in 3D bioprinting and stem cell engineering.
- India: Emerging as a growing hub, with AIIMS, IITs, and NCBS exploring regenerative techniques, especially for skin and bone regeneration.
🧬 How Does Regenerative Medicine Work?
There are three major approaches in regenerative medicine:
1. Stem Cell Therapy
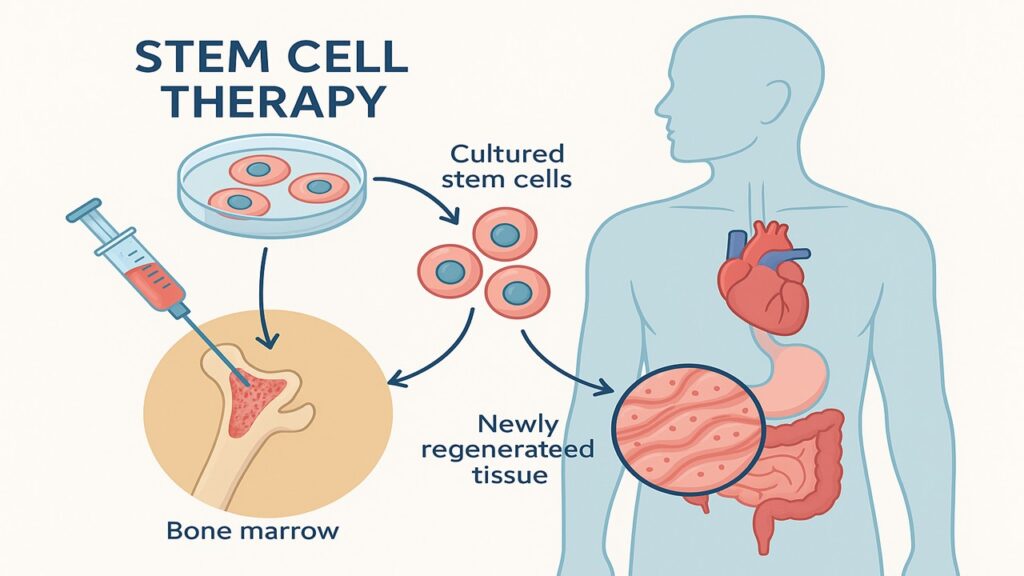
Stem cells, known for their ability to turn into any cell type, are extracted from the patient and grown in the lab. These are then injected into the damaged area (like the heart or spinal cord) to regenerate healthy tissue.
2. Tissue Engineering
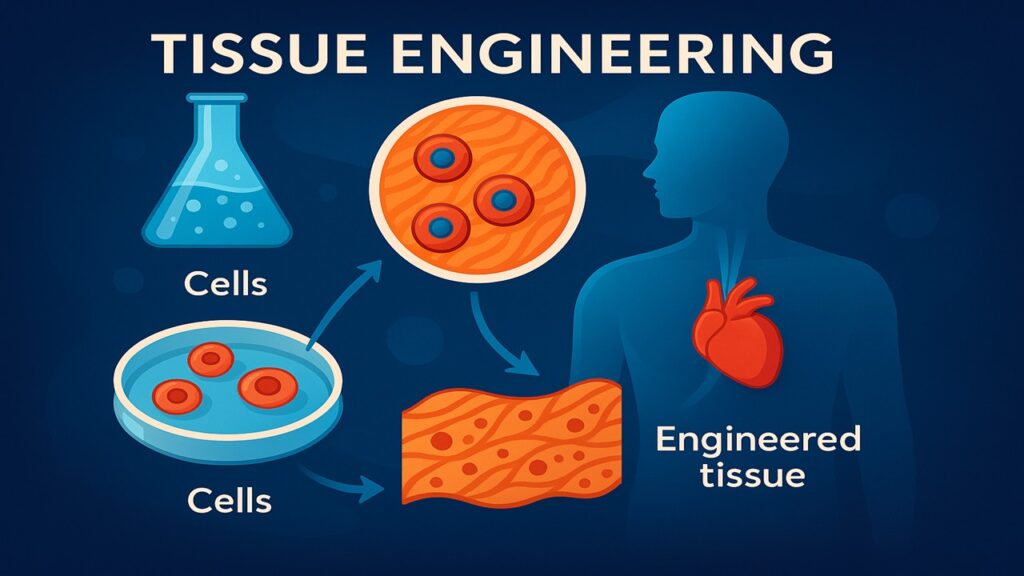
Involves creating scaffolds or “biological frames” that mimic the structure of organs. Living cells are seeded into these scaffolds, where they grow and develop into tissue, ready for implantation.
3. 3D Bioprinting
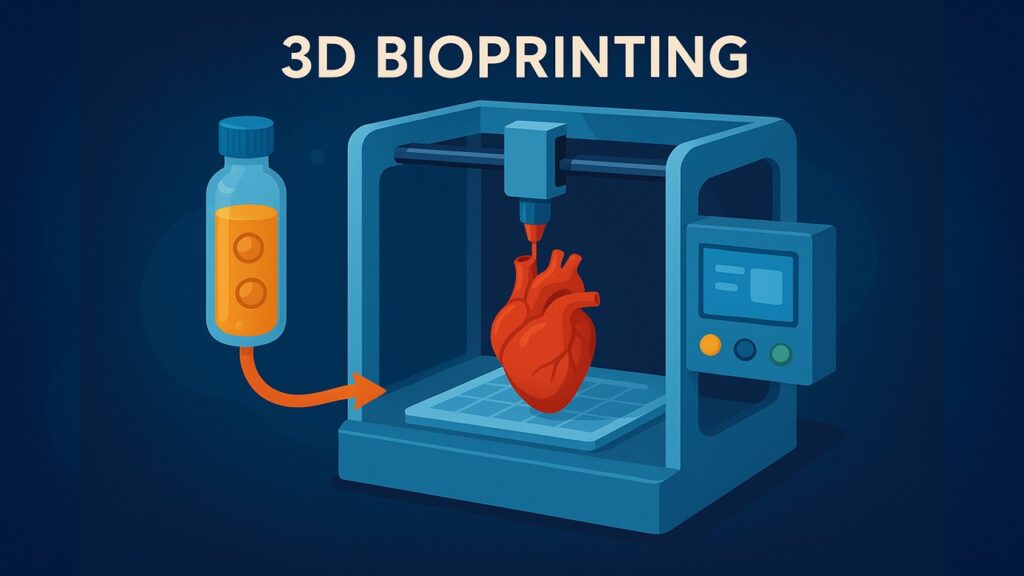
Just like 3D printers create plastic objects, bioprinters use cells and biomaterials to print organ structures layer by layer. These can eventually be implanted in the body once fully functional.
🏥 How Can This Technology Help Patients?
The benefits of regenerative medicine are extraordinary:
- Reduced dependence on organ donors
- Faster recovery from major injuries or burns
- Potential cure for chronic conditions like Parkinson’s, diabetes, and heart failure
- Improved quality of life for accident victims and war veterans
- Minimized risk of transplant rejection, since the organs are built using the patient’s own cells
🔮 What Is the Future of Regenerative Medicine?
Scientists predict that:
- By 2030, organs like skin, bones, and cartilage may be regenerated commonly in labs.
- By 2040, more complex organs like kidneys, livers, and lungs may be commercially grown for transplant.
- Advances in AI and biotechnology will accelerate cell analysis and organ design, making the process faster and more accessible.
- Personalized organ production could become mainstream in leading hospitals worldwide.
What Are the Current Challenges?
While progress is strong, there are challenges:
- High cost of stem cell therapy and bioprinting
- Technical difficulty in producing fully functional organs
- Ethical concerns around embryonic stem cells
- Need for strict regulatory approvals and long-term testing
Despite these, the global medical community remains optimistic that these challenges will be overcome with ongoing research.
💡 Related Breakthroughs in This Field
- iPS Cells (induced pluripotent stem cells)
- Organ-on-a-chip technology
- Smart scaffolding using biodegradable materials
- AI-assisted cell tracking and differentiation
A New Dawn in Healthcare
“Regenerative medicine is not just a technology — it’s a transformation in how we understand healing.
It’s the science of second chances — of giving people the ability to rebuild what they lost, and live a life they once thought impossible.
As science advances, we move closer to a world where every human has the power to heal from within — not through hope alone, but through proven innovation.
The future of healthcare is not about fixing the body… it’s about helping the body fix itself.”