हिंदी में पढ़ने के लिए मेनू बार से हिंदी भाषा चयन करें।
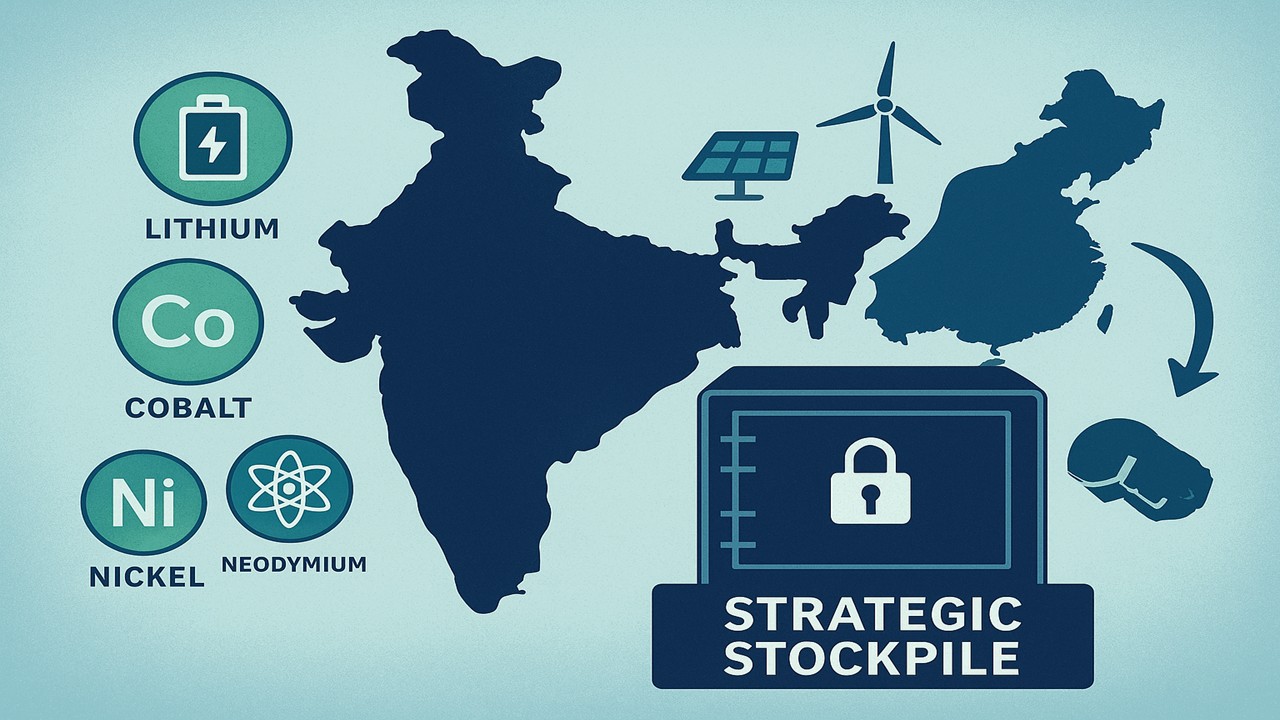
India is set to establish a strategic stockpile of rare earth elements to safeguard its industries from global supply chain disruptions. The plan comes in the wake of rising concerns over China’s export controls on these critical minerals, which are essential for electric vehicles, batteries, defense, and renewable energy technologies.
The stockpile is part of the National Critical Mineral Mission (NCMM), officially launched by the Government of India on April 9, 2025. Under NCMM, the Geological Survey of India (GSI) will conduct 1,200 exploration projects between 2024‑25 and 2030‑31 to map and develop the country’s critical mineral resources.
Why Rare Earth Elements Are Vital
Rare earth elements (REEs) such as lithium, cobalt, nickel, and neodymium are the backbone of modern technologies. Around 60% of the world’s supply comes from China, making India vulnerable to price fluctuations and supply disruptions. By securing a stockpile, India aims to reduce dependency on foreign suppliers and strengthen domestic production.
The Stockpile Plan
The proposed stockpile will initially cover a two-month supply of key minerals. The government is encouraging private sector participation to enhance the initiative’s effectiveness. The stockpile will complement domestic mining efforts in Odisha, Rajasthan, and Jharkhand, and India also plans to import select minerals from trusted international partners.
Benefits for India
- Reduced Import Dependence: Lower reliance on China for critical minerals.
- Industrial Stability: Steady supply and pricing for EV, battery, and defense industries.
- Strategic Autonomy: India can meet its own needs in case of global crises.
- Boost to Make-in-India: Encourages domestic production and exports, creating jobs and investment opportunities.
Current Context
Global supply chains continue to face uncertainty, with China restricting exports of rare earth elements. India’s stockpile plan is a proactive step to ensure that domestic industries remain resilient and future-ready.
Challenges Ahead
Extracting and processing rare earths is technically complex and environmentally sensitive. Long-term storage, inventory management, and recycling capacity will also require careful planning to make the initiative successful.
Outcome:
India’s strategic stockpile initiative is part of a broader effort under NCMM to ensure self-reliance in critical minerals, secure energy transition goals, and protect high-tech industries. While the mission was officially launched in April 2025, recent reports highlight the government’s continuing push to implement the stockpile amid current global supply uncertainties.
Sources: