हिंदी में पढ़ने के लिए मेनू बार से हिंदी भाषा चयन करें।
Introduction
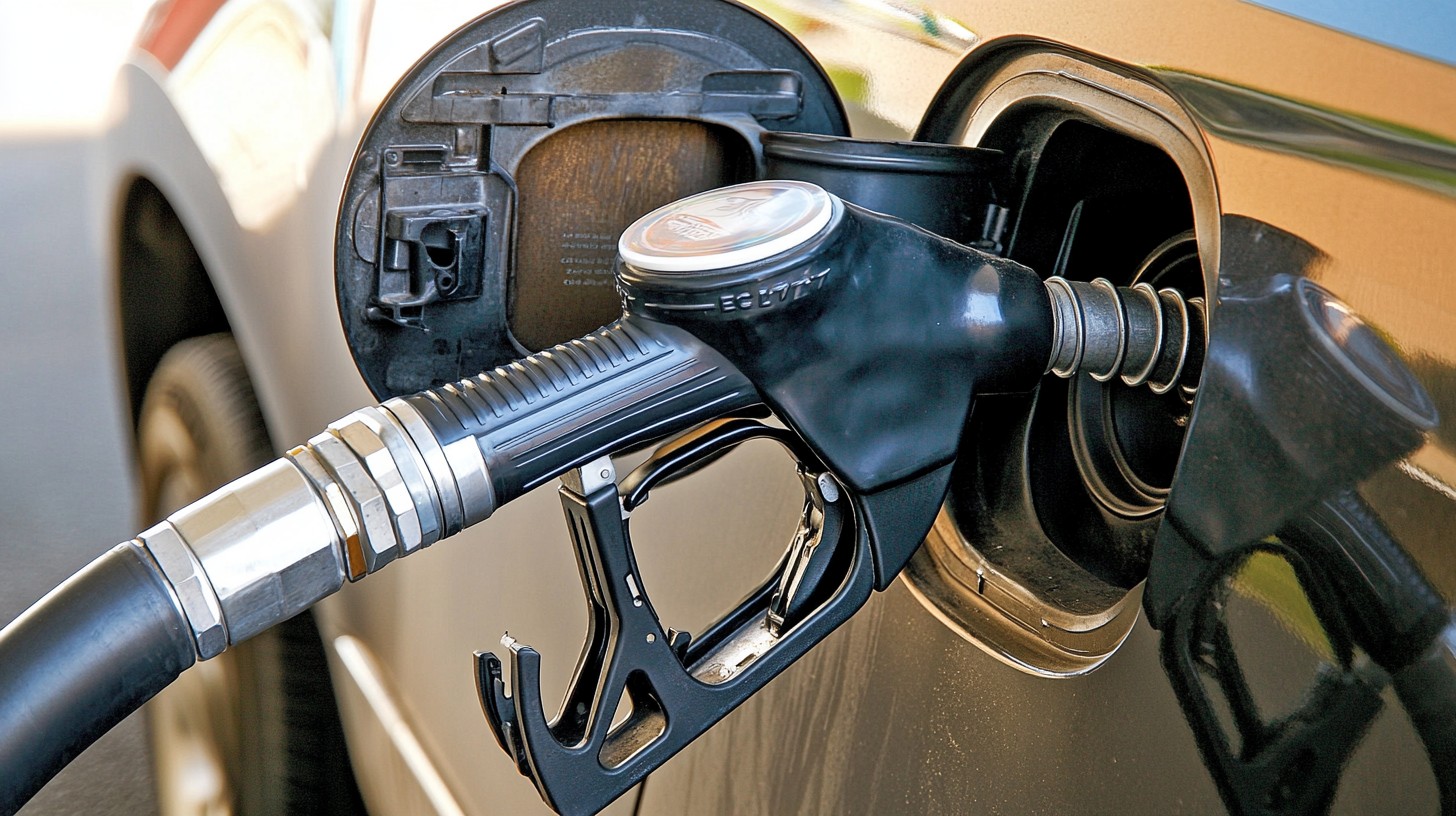
As geopolitical tensions rise in the Middle East—especially between Iran and Israel—India is taking strategic steps to safeguard its energy needs. In recent weeks, the Indian government has significantly increased crude oil imports from Russia and the United States. This move is seen as a clear indication of India’s strategy to ensure energy security while maintaining supply stability during uncertain global conditions.
Why Is This Decision Important?
The Middle East has long been India’s major source of crude oil. However, the ongoing conflict between Iran and Israel, combined with U.S. strikes in the region, has triggered serious concerns over supply chain disruptions and price volatility.
To avoid any oil supply crisis and price shocks in the domestic market, India is:
- Diversifying its import sources
- Strengthening energy ties with countries like Russia and the U.S.
- Reducing over-dependence on the Gulf region
India’s Oil Import Strategy at a Glance
| Country | Current Import Share (Approx.) | Trend |
| Russia | 35% | 📈 Rising |
| USA | 12% | 📈 Rising |
| Iraq | 18% | 📉 Slight Dip |
| Saudi Arabia | 14% | 📉 Declining |
| Iran | <1% (Due to sanctions) | 🔒 Restricted |
✅ Russia has become India’s top oil supplier, thanks to discounted rates post-Ukraine war.
✅ The USA is now among the top 5 suppliers to India, offering a secure, long-term alternative.
Government’s Perspective
Union Petroleum Minister Hardeep Singh Puri recently said:
“India has sufficient fuel supplies for the coming weeks. The government is closely monitoring the global situation and will take all necessary steps to maintain domestic stability.”
This statement clearly signals confidence in India’s import strategy and the country’s preparedness to manage oil availability despite geopolitical risks.
Benefits of This Strategy
1. Energy Security
By diversifying suppliers, India protects itself from sudden disruptions in the Middle East.
2. Cost Advantage
Russian crude oil is being imported at discounted prices, helping reduce the trade deficit and control domestic fuel inflation.
3. Strategic Reserves
Increased imports also help India refill its Strategic Petroleum Reserves (SPR)—important for emergencies.
Challenges and Risks
- Logistics: Longer shipping distances from the U.S. and Russia increase transportation costs.
- Sanction Risk: Heavy reliance on Russian oil could attract pressure from Western countries.
- Price Volatility: Any escalation in the Iran-Israel war can still impact global oil prices.
What It Means for Indian Consumers
Despite rising global tensions, Indian consumers have so far been shielded from major fuel price hikes. This is due to:
- Government’s smart procurement from alternative markets
- Oil companies absorbing minor cost increases
- Stable rupee-dollar exchange rate supporting import bills
But if the conflict worsens, prices may rise in the coming weeks.
India’s decision to increase oil imports from Russia and the U.S. reflects a calculated and proactive approach to ensure uninterrupted energy supplies. At a time when the Middle East is facing severe instability, India’s move highlights its energy diplomacy strength and commitment to protecting its citizens from global fuel shocks.
By strengthening its international energy partnerships, India is moving towards becoming a more resilient and self-reliant energy consumer in the global economy.
Source: Times of India, Ministry of Petroleum & Natural Gas, Reuters