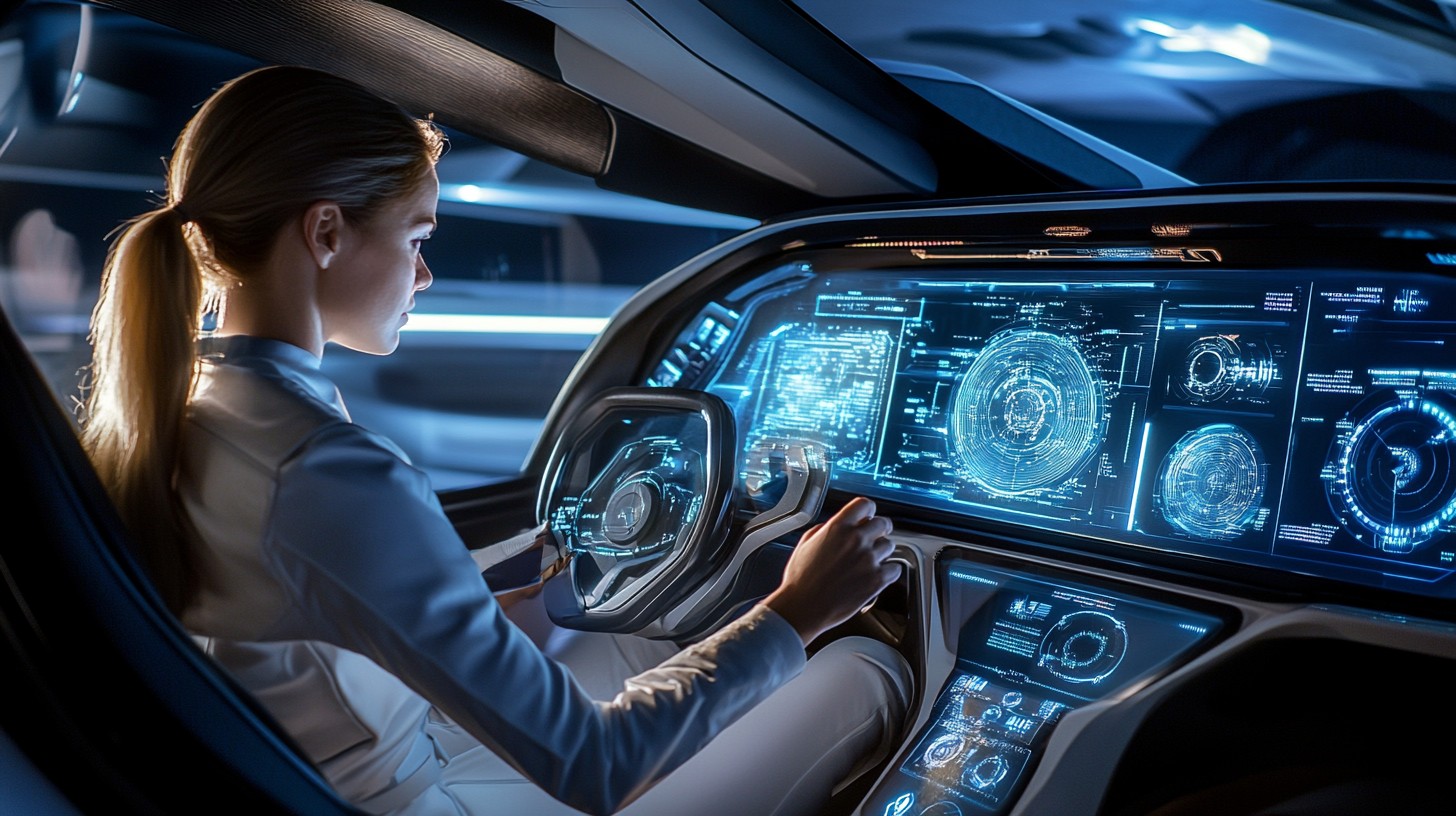
Autonomous driving technology is a revolutionary advancement that is transforming the way we think about transportation. It refers to vehicles that can navigate, drive, and make decisions without human input. This is achieved through a combination of advanced technologies like sensors, cameras, artificial intelligence (AI), and machine learning. Let’s break this down step by step to understand it better.
Key Components of Autonomous Driving
Sensors:
Autonomous vehicles are equipped with a variety of sensors, such as radar, lidar, and ultrasonic sensors. These help the vehicle detect nearby objects, pedestrians, other cars, and road conditions.
- Radar: Uses radio waves to detect objects and their speed.
- Lidar: Uses lasers to measure the distance between the vehicle and surrounding objects, helping create a 3D map of the environment.
- Ultrasonic Sensors: Used for close-range detection, such as parking assistance.
Cameras:
These are placed around the vehicle to provide visual data. Cameras help in reading road signs, detecting lane markings, and identifying obstacles such as pedestrians, bicycles, or other vehicles.
Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning:
AI is the brain behind autonomous vehicles. It processes the data collected by the sensors and cameras and makes decisions in real time. Machine learning allows the system to improve its performance over time by learning from its past experiences, making it smarter with each drive.
Navigation Systems:
GPS and high-definition mapping technologies are used to accurately determine the vehicle’s location and guide it on the road. This helps the car to follow routes and navigate through different terrains or cities.
Connectivity:
Autonomous vehicles can communicate with each other and with infrastructure (like traffic signals) through Vehicle-to-Everything (V2X) communication. This helps in better coordination and reduces the risk of accidents.
Levels of Autonomy
There are five levels of autonomous driving, which describe the extent to which a vehicle can operate without human intervention:
Level 0: No automation – the driver is in complete control.
Level 1: Driver assistance – basic systems like cruise control.
Level 2: Partial automation – the car can control speed and steering but requires driver supervision (e.g., Tesla Autopilot).
Level 3: Conditional automation – the vehicle can handle most driving tasks but may need human intervention in certain conditions.
Level 4: High automation – the vehicle can operate in most conditions without human intervention, but a human can take over if necessary.
Level 5: Full automation – the vehicle can drive in any condition without any human input.
How Autonomous Cars Work:
Autonomous vehicles rely on a combination of technologies to understand their environment and make decisions. They continuously scan their surroundings, identify obstacles, plan routes, and adjust their speed and direction. Here’s how it works in a simple flow:
- Data Collection: The vehicle’s sensors, cameras, and GPS collect real-time data about the surroundings (other vehicles, road signs, pedestrians, etc.).
- Processing: AI systems process this data, analysing everything happening around the vehicle. Machine learning algorithms predict the behaviour of other objects (e.g., cars or people crossing the road).
- Decision Making: Based on the data, the AI decides how the vehicle should respond. For example, it may slow down, change lanes, or stop if it detects a hazard.
- Action: The vehicle’s control systems carry out the decisions by steering, accelerating, or braking.
Companies Leading the Autonomous Driving Revolution
Several companies are investing heavily in autonomous driving technology. Here’s a look at some of the leaders:
- Tesla: Tesla’s Autopilot and Full Self-Driving (FSD) capabilities have made it one of the most prominent names in autonomous technology. Tesla continuously updates its software to improve its cars’ ability to handle more complex driving tasks.
- Waymo: A subsidiary of Alphabet (Google’s parent company), Waymo is a pioneer in self-driving cars. It operates a fleet of autonomous taxis in several U.S. cities and has logged millions of miles of testing.
- Cruise: Owned by General Motors, Cruise is focused on developing autonomous electric vehicles. The company is working on making urban transportation safer and more efficient through fully autonomous ride-sharing services.
- Aurora: This company is working on self-driving technology for various sectors, including passenger vehicles, trucks, and even logistics. Aurora aims to make transportation safer and more accessible.
- Nvidia: While not directly making cars, Nvidia plays a key role in providing the computing power for many autonomous driving systems. Its AI chips are used by several automakers to process the enormous amounts of data needed for self-driving.
- Apple: Apple’s secretive Project Titan aims to develop its own autonomous electric vehicle. While little is known, Apple is reportedly focusing on creating an advanced car with cutting-edge technology.
Impact of Autonomous Driving on the Future
- Safety: One of the biggest promises of autonomous driving is reducing accidents caused by human error, which account for the majority of traffic incidents today.
- Efficiency: Autonomous vehicles can optimize routes, reduce fuel consumption, and decrease traffic congestion by communicating with each other.
- Accessibility: Self-driving cars can provide mobility to people who cannot drive, such as the elderly or disabled.
- Economic Shift: The rise of autonomous vehicles will have significant implications for industries like insurance, logistics, public transport, and ride-hailing services.
Challenges Ahead
Despite the potential, there are still several challenges before fully autonomous vehicles become mainstream:
Regulatory Hurdles:
Governments around the world are still figuring out how to regulate autonomous vehicles.
Public Trust:
Building public trust in the safety and reliability of self-driving cars is crucial.
Technical Challenges:
Navigating complex environments, bad weather conditions, and unpredictable human behaviour still pose challenges for the technology.
Autonomous driving technology is still in development, but as companies continue to innovate, it is only a matter of time before these vehicles become a common part of our roads.