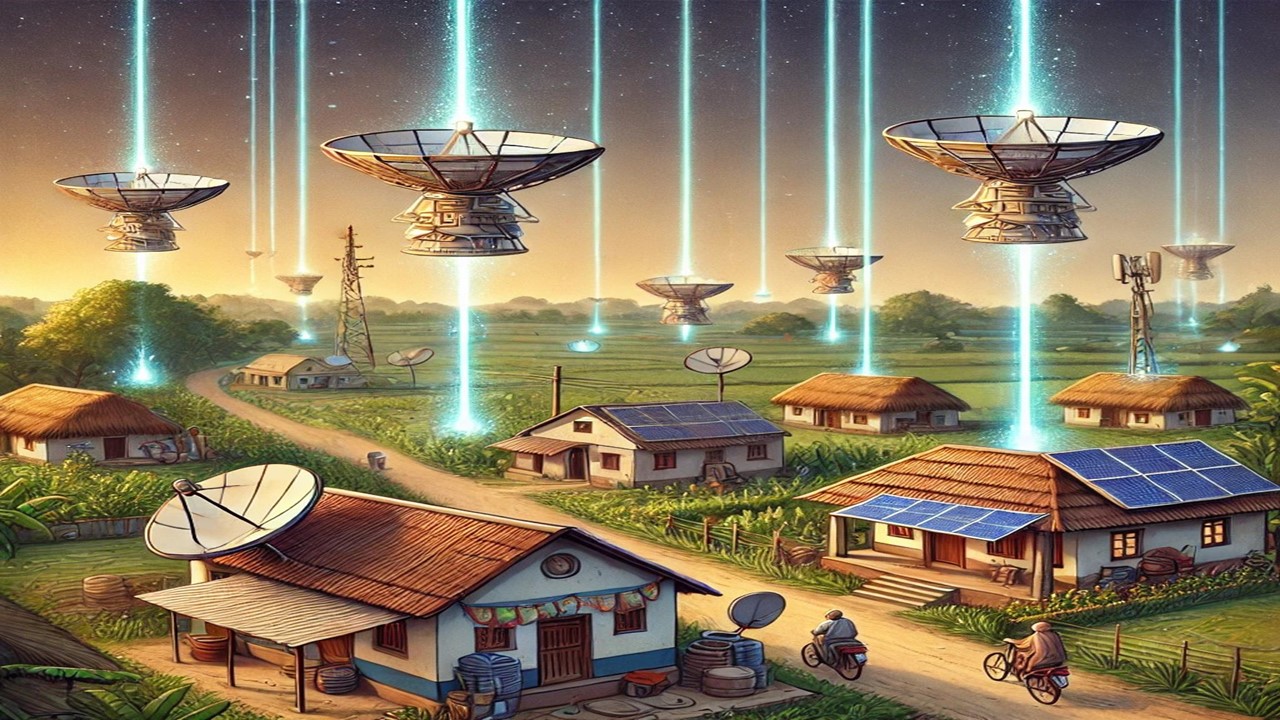
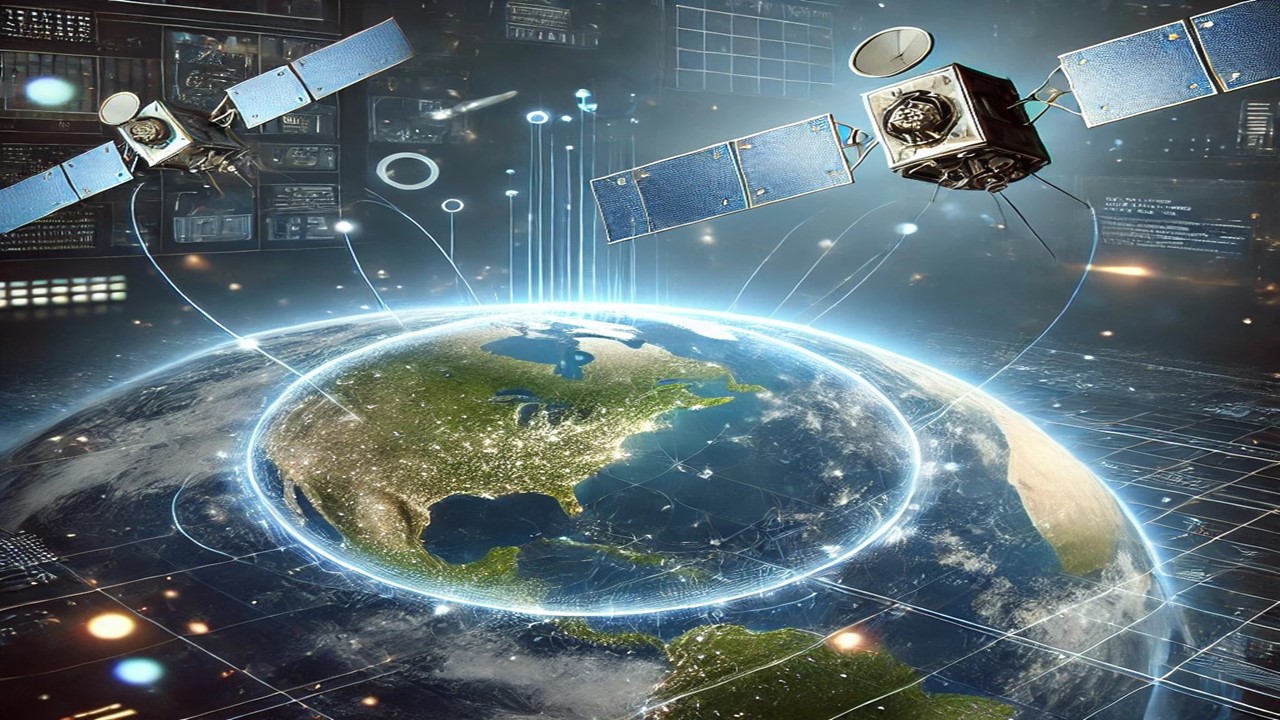
Starlink, an ambitious project by SpaceX, was launched with the goal of providing high-speed internet connectivity to remote and rural areas across the world. Announced in 2015 by Elon Musk, Starlink aims to deliver reliable and affordable internet connectivity globally, reducing the digital divide between urban and rural areas.
In this article, we’ll understand how Starlink works, its unique technologies, and its potential future in India.
How Starlink Works
Starlink operates through a network of small satellites in low Earth orbit (LEO), positioned about 550 kilometers above the Earth. These satellites receive signals from ground stations and directly transmit data to user locations through a dish antenna. Unlike traditional satellite internet services, Starlink’s use of low Earth orbit significantly reduces latency, making it more efficient for real-time applications.
- LEO Satellites: Starlink’s satellites are positioned in low Earth orbit at an altitude of 550 km. This closer orbit helps keep latency low, which is beneficial for gaming and real-time video calls.
- Dish Antenna: A specially designed dish antenna for Starlink connects directly to the satellites, ensuring high-speed internet connectivity. The antenna automatically stays in sync with the satellites.
- Ground Stations: These stations are the primary source of internet for the satellites, allowing data to flow between ground and sky. Strategic placement of ground stations enhances Starlink’s stable and fast connectivity.
- Mesh Network: Starlink employs a mesh network. This means if one satellite’s signal is weak, another satellite takes over to provide seamless connectivity.
Key Features of Starlink
Starlink stands out from traditional internet services due to its unique features, establishing it as a revolutionary step in internet connectivity:
- High-Speed Internet: Starlink offers speeds between 100 Mbps and 200 Mbps, significantly faster than traditional satellite internet.
- Low Latency: Since it operates in low Earth orbit, Starlink offers lower latency compared to traditional satellites, which is beneficial for video calls and online gaming.
- Global Coverage: Starlink’s primary goal is to provide internet connectivity to remote and rural areas worldwide.
- User-Friendly Dish Antenna: Starlink’s self-installing dish antenna adjusts automatically to connect with the best signal from satellites.
Starlink’s Future in India
Starlink has the potential to bring new digital and technological opportunities to India. However, there are challenges and opportunities that could impact the widespread adoption of this technology.
1. Improved Connectivity in Rural and Remote Areas
India’s rural and remote areas often have limited internet connectivity. Starlink’s mission to provide reliable, high-speed internet to even the most isolated regions can be transformative for India’s underdeveloped areas. Without internet access, knowledge and economic growth are limited, and Starlink could play a key role in bridging this gap.
2. Contribution to Digital India and Aatmanirbhar Bharat Goals
Starlink can support India’s Digital India and Aatmanirbhar Bharat missions by reducing the gap in technology and digital services between rural and urban areas. With reliable internet access, people can benefit from e-learning, telemedicine, and digital payments. Starlink, in partnership with Digital India, could foster new business and entrepreneurial opportunities.
3. Improvement in Education and Healthcare Sectors
High-speed internet connectivity can improve the quality and accessibility of education and healthcare services in remote areas. Students will be able to take advantage of online courses and virtual classrooms, while telemedicine can enhance communication and treatment between doctors and patients.
4. Connectivity During Natural Disasters
Starlink’s satellite-based connectivity can be extremely helpful during natural disasters when ground-based infrastructure may fail. In the aftermath of events like floods, earthquakes, and cyclones, Starlink can act as a reliable source of connectivity to aid relief operations and communication.
5. Challenges and Regulatory Issues
In India, satellite-based internet services require approval from the Telecom Regulatory Authority of India (TRAI) and the Department of Telecommunications (DoT). The regulatory approval process presents certain challenges that could delay Starlink’s rollout. If SpaceX navigates these regulations successfully, the launch of Starlink in India could become more feasible.
6. Competition from Local Internet Providers and Projects
India already has broadband and 4G/5G providers like Jio, Airtel, and BSNL offering affordable plans. Starlink would need to match or exceed these providers in terms of cost and service quality to stay competitive. It may be challenging for Starlink to establish itself as a viable alternative, especially for users in rural and semi-urban areas.
7. India’s Own Satellite Internet Mission
India’s space agency, ISRO, is also stepping into the satellite-based internet sector. ISRO’s collaboration with OneWeb to provide satellite internet in rural and remote areas could offer an affordable alternative, creating competition for Starlink in India.
Overall
The future of Starlink in India is promising but depends on several factors, including regulatory approvals, cost, and competition. High-speed connectivity could boost e-learning, telemedicine, and new business models in rural and underserved areas of India. However, Starlink may face significant challenges such as high setup costs, regulatory hurdles, and competition from existing internet providers.
If SpaceX can overcome these challenges and make its internet services accessible and affordable, Starlink could herald a new digital revolution in India. The impact of Starlink would not be limited to connectivity alone; it could also contribute significantly to India’s technological and economic growth.