हिंदी में पढ़ने के लिए मेनू बार से हिंदी भाषा चयन करें।
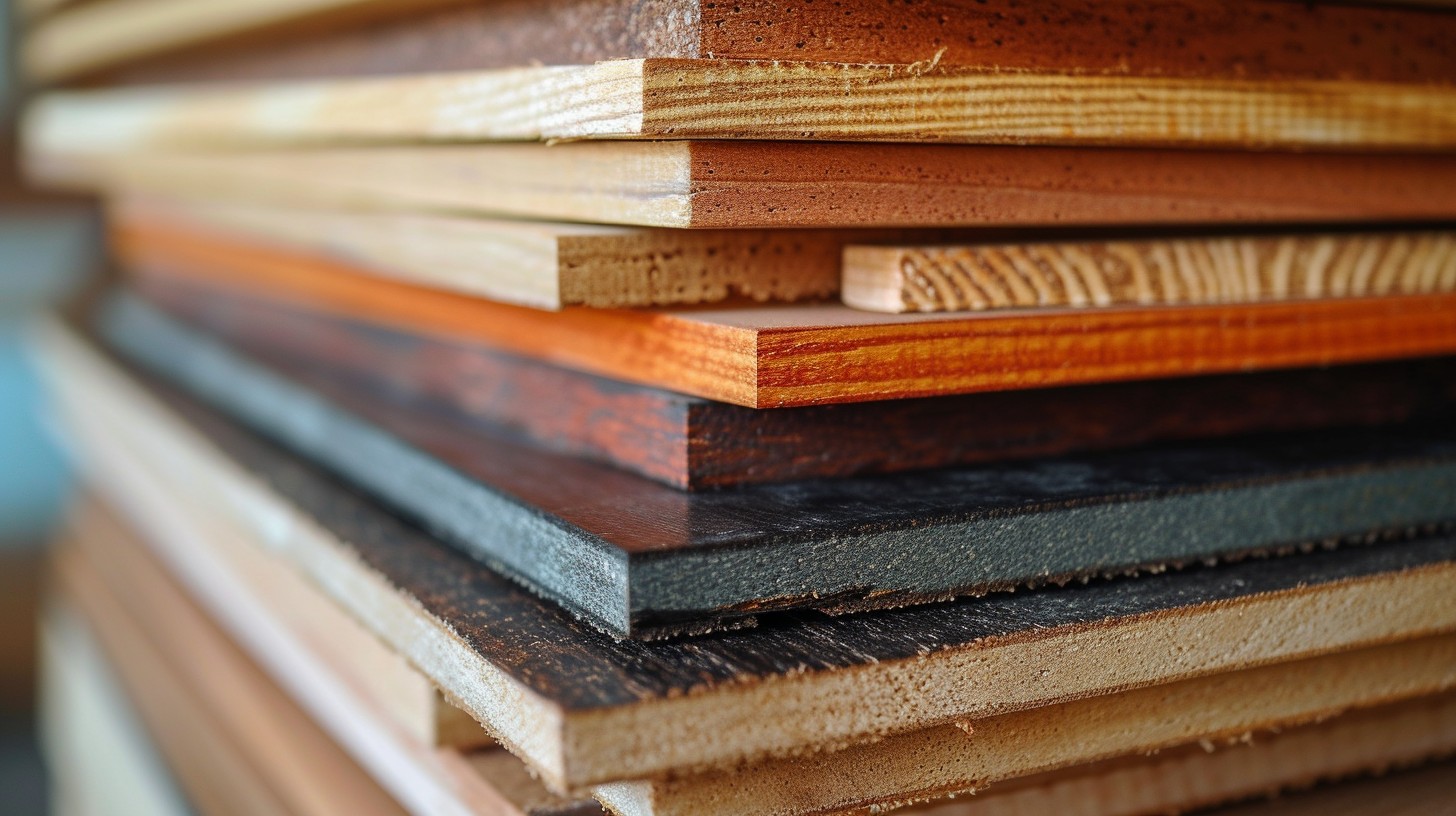
Plywood. A word so common that it hardly sparks curiosity. Yet, beneath its seemingly simple surface lies a world of intrigue, innovation, and immense global importance. What if I told you that the material supporting your furniture, floors, and even walls holds a story as layered as its structure? Let’s peel back the layers and uncover the tale of plywood—its creation, its impact, and its future.
Why Plywood Matters
Picture this: You walk into a room, the warm tones of wood exuding comfort and luxury. Yet, it isn’t solid wood; it’s plywood, a material engineered to perfection. But why plywood and not natural wood? The answer lies in its unmatched versatility, durability, and cost-efficiency. Plywood has become the backbone of modern architecture and design, but how did it achieve this stature? To understand its global dominance, we must first explore how it’s made.
The Birth of Plywood: An Ingenious Process
Creating plywood is no ordinary process. It’s an art and science combined, perfected over decades. Here’s how it unfolds:
- Log Selection: It all begins with selecting high-quality logs from trees like eucalyptus, poplar, birch, or teak. Each type of wood offers unique properties, determining the plywood’s strength, appearance, and durability.
- Debarking: The selected logs are stripped of their bark using advanced machinery to ensure smooth, defect-free veneers.
- Slicing into Veneers: The logs are then rotated and sliced into thin sheets, called veneers, using a lathe machine. These sheets are only a few millimeters thick but hold the essence of the log’s strength.
- Drying: The veneers are dried in large industrial dryers to remove moisture, ensuring they bond well in the next stages.
- Layering: Veneers are stacked in layers, with each layer’s grain direction alternating. This cross-graining technique provides plywood with its exceptional strength and resistance to warping.
- Gluing and Pressing: The layers are bonded using strong adhesives like phenol-formaldehyde or urea-formaldehyde. High pressure and heat solidify the bond, transforming the stack into a unified panel.
- Trimming and Finishing: The rough edges are trimmed, and the surface is sanded to achieve a smooth finish. Some panels may undergo additional treatments like lamination or chemical coating for enhanced properties.
The Global Market: Demand and Supply Dynamics
Plywood isn’t just a material; it’s a global commodity. Its demand spans continents, driven by construction, furniture, packaging, and automotive industries. Let’s explore its global and Indian market dynamics:
Worldwide Market Capitalization
The global plywood market is valued at over $70 billion and growing at a steady pace, fueled by rapid urbanization and construction booms in developing countries. Regions like North America, Europe, and Asia-Pacific dominate consumption, with China emerging as the largest producer and exporter.
India’s Role
India, too, plays a significant part. With a market value of over ₹10,000 crore, Indian plywood manufacturers cater to both domestic and international demands. The rise in housing projects, modular furniture, and eco-friendly initiatives has further boosted its growth.
Industry Giants: Who’s Leading the Pack?
When it comes to plywood manufacturing, a few names stand tall, both globally and in India:
Global Leaders
- Georgia-Pacific (USA): Known for high-quality plywood and wood products.
- Boise Cascade (USA): A leader in engineered wood solutions.
- UPM-Kymmene (Finland): A pioneer in sustainable plywood production.
Indian Titans
- Century Plyboards: A household name offering a wide range of plywood and laminates.
- Greenply Industries: Renowned for eco-friendly and premium quality plywood.
- Kitply Industries: Among the oldest and most trusted brands in India.
- Sarda Plywood Industries: Known for its flagship brand, ‘DURO.’
The Future of Plywood: Innovation and Sustainability
As we venture into the future, plywood manufacturing is undergoing remarkable transformations:
Research and Development
- Eco-Friendly Adhesives: Scientists are exploring plant-based adhesives to replace formaldehyde-based ones, reducing environmental impact.
- Fire-Resistant Plywood: Advanced treatments are making plywood more resistant to fire, increasing its safety in construction.
- Lightweight Panels: Research is focused on creating lighter yet stronger panels for specialized applications like aviation and automotive industries.
Technological Advancements
- Automation: Robotics and AI are streamlining the manufacturing process, ensuring precision and efficiency.
- Digital Grading: Advanced scanners are now grading veneers for defects, enhancing overall quality.
Sustainability Initiatives
- Recycled Wood: Many manufacturers are using wood waste to create high-quality plywood, promoting circular economies.
- Carbon Neutrality: Efforts are underway to make plywood factories carbon-neutral through renewable energy and waste management.
A Glimpse into the Future
The plywood industry is poised for tremendous growth, with sustainability and innovation leading the way. In India, the push towards green buildings and modular furniture will drive demand. Globally, advancements in engineered wood technology promise to unlock new possibilities. Plywood’s journey, from ancient Egyptian furniture to modern skyscrapers, is far from over. As it evolves, it continues to support our lives, quite literally, from the ground up.
A Material Worth Its Layers
Plywood is more than just a construction material; it’s a testament to human ingenuity and adaptability. Its layered structure symbolizes its layered significance in our daily lives. From your home’s foundation to the furniture you cherish, plywood silently supports and enriches your world. And as the industry marches towards a greener, smarter future, one thing is certain: the story of plywood will remain as timeless as the material itself.